Risk of myocardial infarction based on endothelial shear stress analysis using coronary angiography
Wall shear stress (WSS) has been associated with atherogenesis and plaque progression.
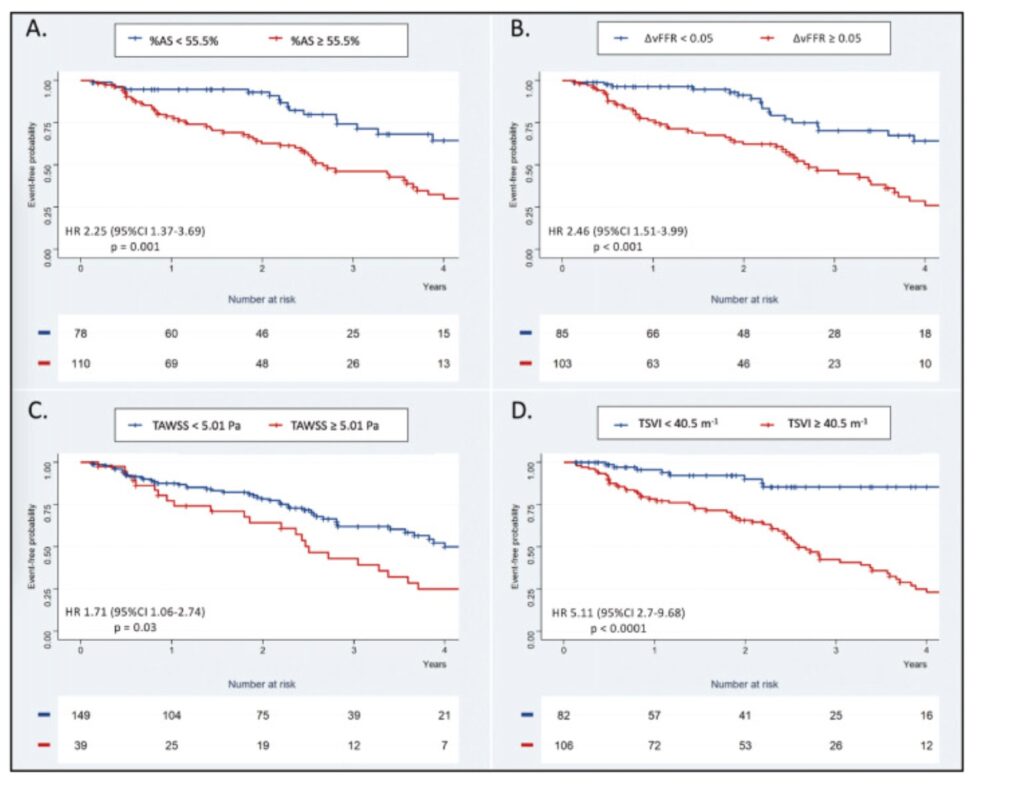
The present study assessed the value of WSS analysis derived from conventional coronary angiography to detect lesions culprit for future myocardial infarction (MI).
The show that although angiography-derived anatomical lesion severity and pressure drop along the vessel showed capacity in identifying coronary lesions leading to MI, the extension of the functional evaluation to include angiographic derived endothelial shear stress features – TAWSS and TSVI – improved the predictive capacity for MI.
Reference
Alessandro Candreva,Mattia Pagnoni,Maurizio Lodi Rizzini,Takuya Mizukami,Emanuele Gallinoro,Valentina Mazzi,Diego Gallo,David Meier,Toshiro Shinke,Jean-Paul Aben,Sakura Nagumo,Jeroen Sonck,Daniel Munhoz,Stephane Fournier,Emanuele Barbatoa,Ward Heggermont,Stephane Cook,Claudio Chiastra,Umberto Morbiducci,Bernard De Bruyne,Oliver Muller,Carlos Collet, "Risk of myocardial infarction based on endothelial shear stress analysis using coronary angiography", Atherosclerosis, Published Online (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2021.11.010.
Go To the Journal Page