Dissipative energy loss within the left ventricle detected by vector flow mapping in children: Normal values and effects of age and heart rate
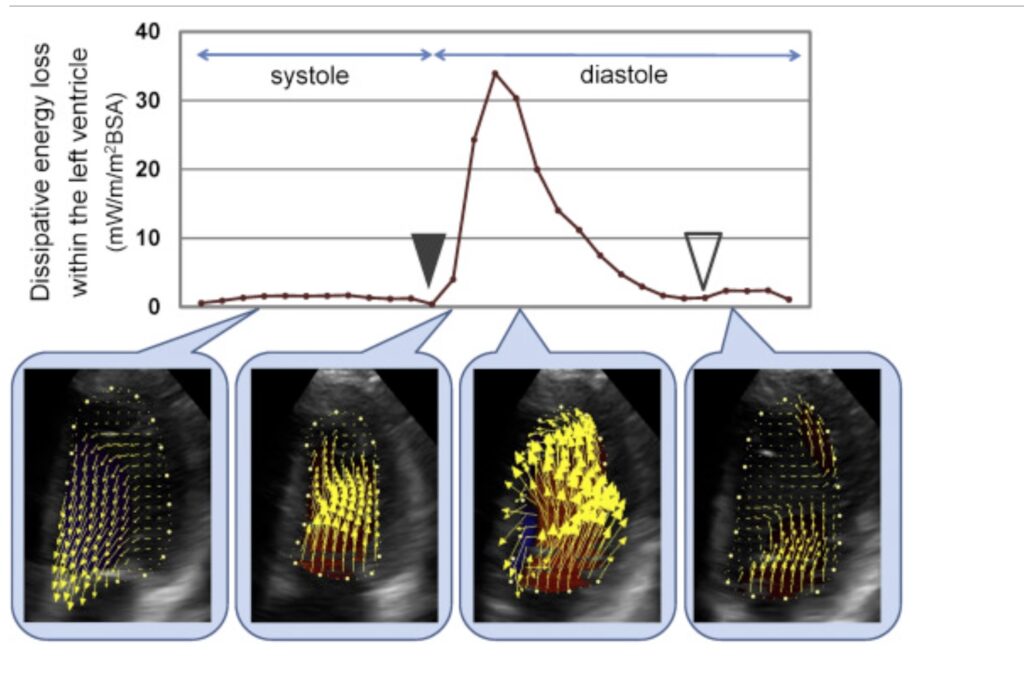
Dissipative energy loss (EL) derived from the velocity vector field of intraventricular blood flow is considered to reflect the efficiency of blood flow, and could be an indicator of left ventricular function.
They aimed to determine the reference values of the EL derived from VFM within the left ventricle.
The result that the systolic and diastolic EL were positively correlated with heart rate (HR) and negatively correlated with age. Moreover, the diastolic EL was positively correlated with the E wave peak velocity.
Reference
Taiyu Hayashi MD, Keiichi Itatani MD,PhD,Ryo Inuzuka MD,PhD,Nobutaka Shimizu MD,PhD, Takahiro Shindo MD, Yoichiro Hirata MD,PhD, Kagami Miyaji MD,PhD, "Dissipative energy loss within the left ventricle detected by vector flow mapping in children: Normal values and effects of age and heart rate", Journal of Cardiology, 66 (2015) 403-410.
Go To the Journal Page